What Was The Crop Lien System
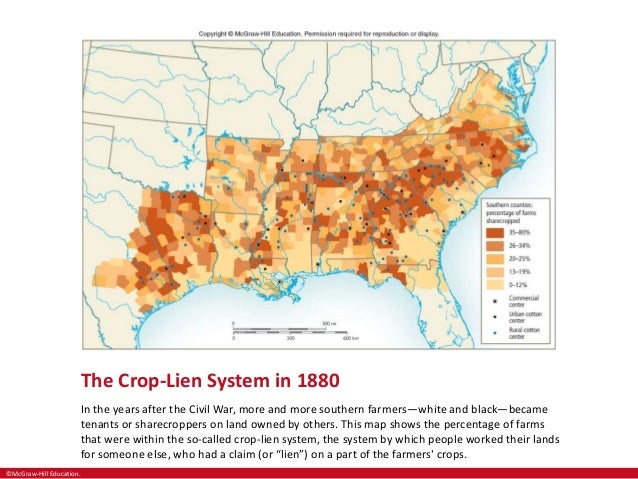
What was the crop lien system. The crop-lien system and sharecropping contributed to the greater shift in Southern agriculture towards one-crop farming. The crop-lien system was a credit system that became widely used by cotton farmers in the United States in the South from the 1860s to the 1930s. They would obtain credit for this rental based on the crops they would produce during the next growing season.
When the cotton crop was harvested. However this system was putting former slaves and land owners into debt. Western farmers sold fruit as their main cash crop.
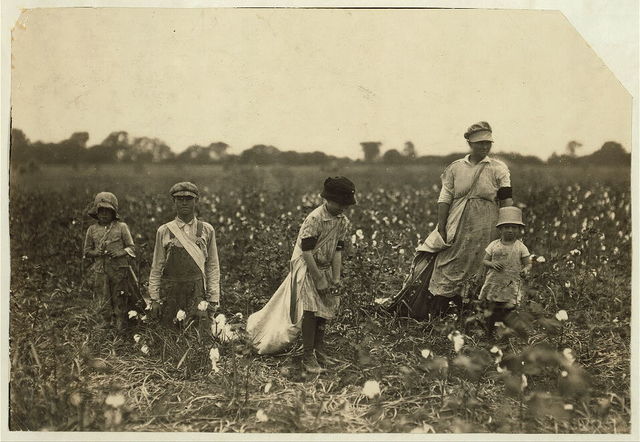
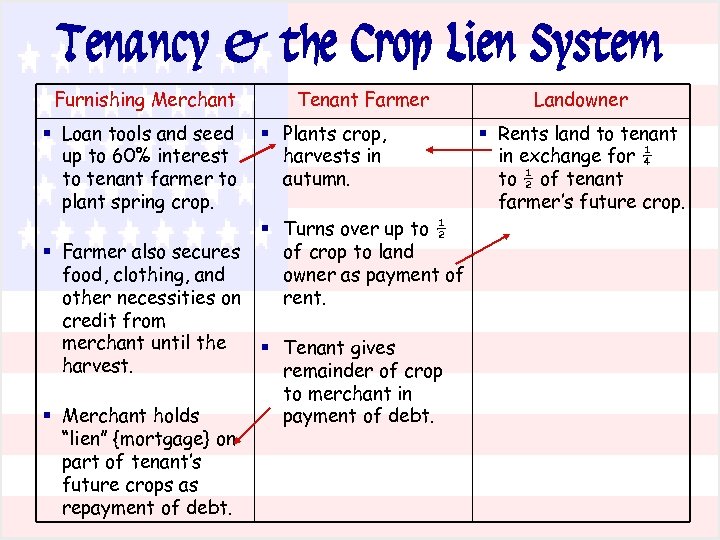
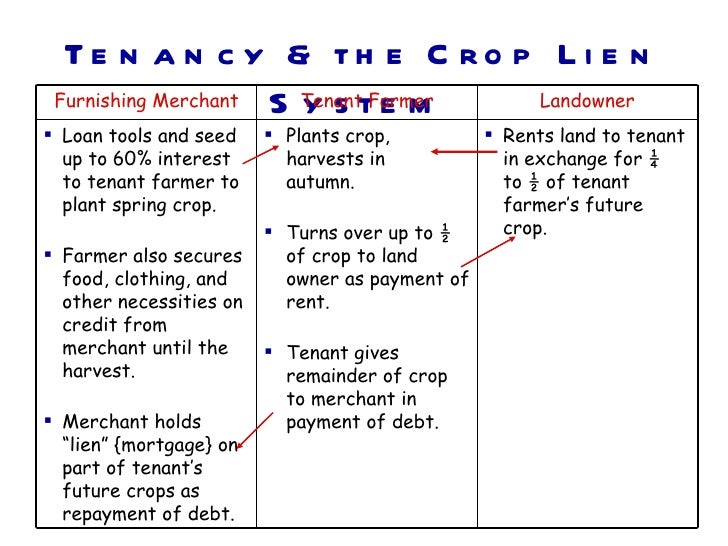
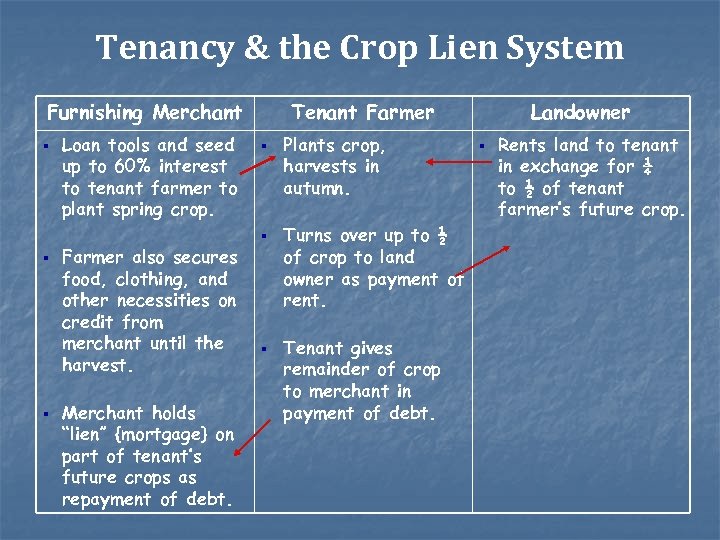
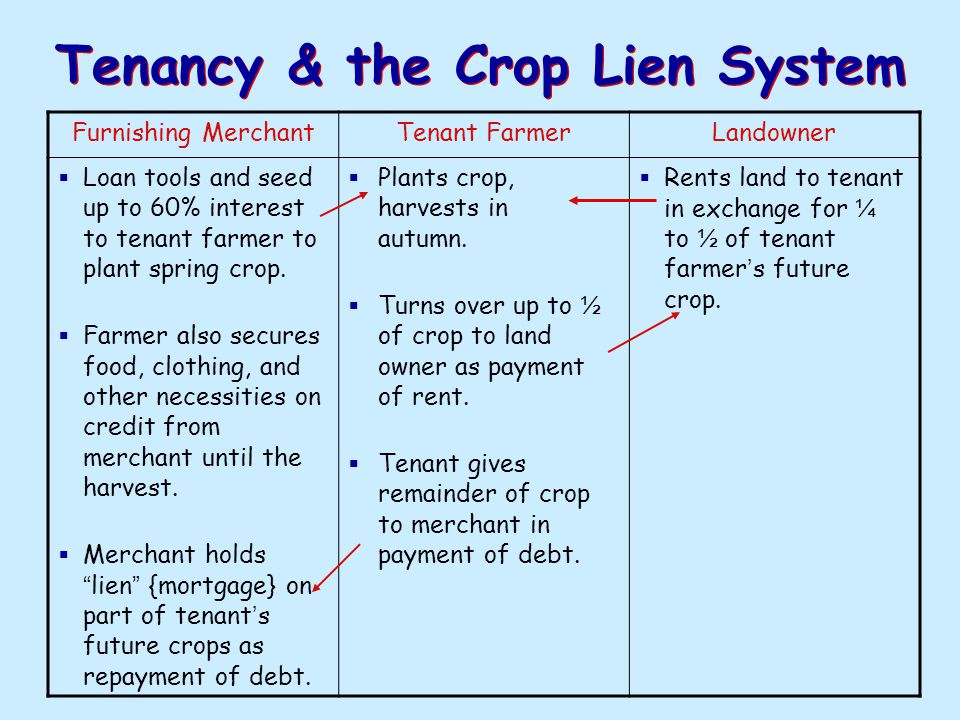
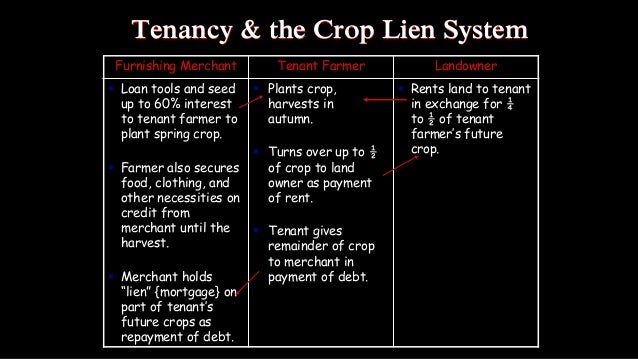
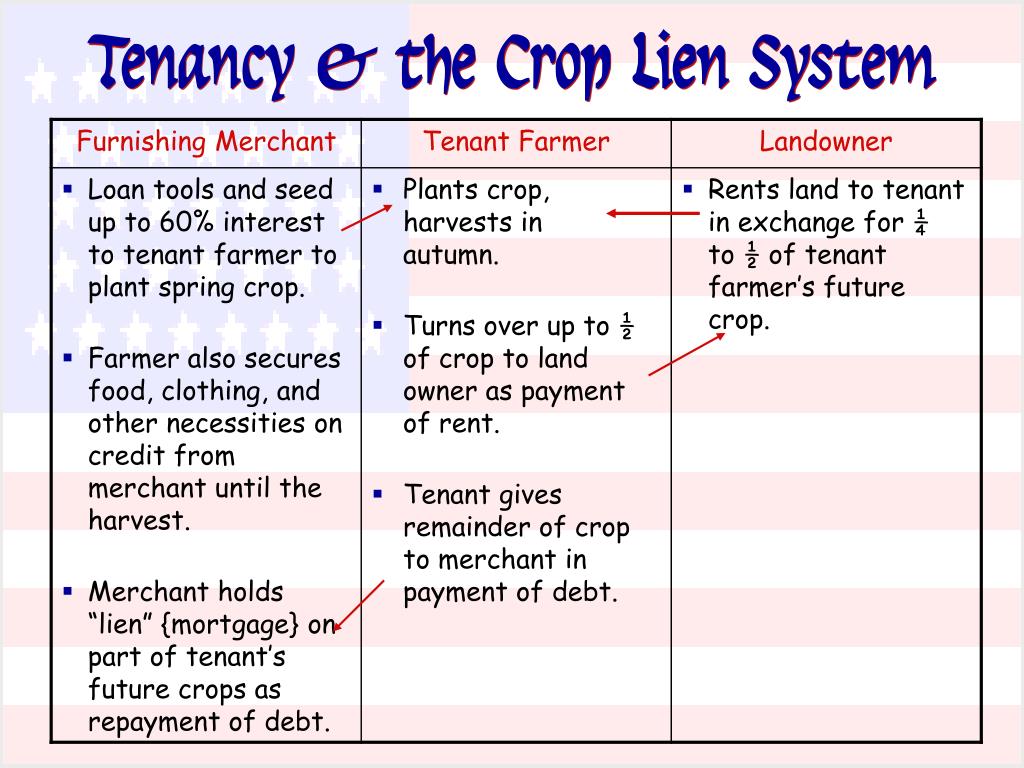
Local merchants provided food and supplies all year long on credit. Aa system in which farmers promised to pay for goods with earnings from future crops B a system in which farmers rented land from a landowner in return for a share of the crop C a system in which farmers stored a crop until the price increased enough to. Sharecroppers and tenant farmers who did not own the land they worked obtained supplies and food on credit from local merchants.
The only ones making profit were the bankers. By providing credit until crops were harvested merchants were allowed to charge higher prices for such purchases-usually adding a markup of 20 to 50 percent but in some cases much higher. Sharecroppers and tenant farmers who did not own the land they worked obtained supplies and food on credit from local merchants.
The crop-lien system was a way for farmers to get credit before the planting season by borrowing against the value for anticipated harvests. The merchants held a lien on the cotton crop and the merchants and. The crop-lien system gave farmers a line of credit with a local merchant for supplies with repayment to be made when a farmers crop was sold.
The crop-lien system was another way Southerners tried to boost their economy. The Crop Lien System. Sharecroppers and tenant farmers who did not own the land they worked obtained supplies and food on credit from local merchants.
Under the crop lien system farmers could get fertilizer farming equipment groceries and other goods by giving merchants a lien on their cash crops the most desirable being cotton and tobacco. Because of their growing indebtedness and sharecropping many farmers had to turn from subsistence agriculture which had once been the norm to cash crops in order to pay off their loans.
Gain voting rights at the state level first and then move on to federal rights.
However this system was putting former slaves and land owners into debt. The crop-lien system was a credit system that became widely used by cotton farmers in the United States in the South from the 1860s to the 1930s. The debt was to be repaid after. The only ones making profit were the bankers. What was the crop-lien system. Bar men from membership in their organization and gain immediate womens suffrage. The former slaves would get paid five dollars on a good year and the merchants. The crop-lien system was a way for farmers to get credit before the planting season by borrowing against the value for anticipated harvests. Crop-lien system Last updated January 25 2020.
The crop-lien system was a credit system that became widely used by cotton farmers in the United States in the South from the 1860s to the 1930s. Western farmers sold fruit as their main cash crop. The crop-lien system was a way for farmers to get credit before the planting season by borrowing against the value for anticipated harvests. In exchange for seeds food tools and other necessities farmers would provide a lien on their crops from the next harvest. Crop-lien system Last updated January 25 2020. The crop-lien system was another way Southerners tried to boost their economy. The crop-lien system and sharecropping contributed to the greater shift in Southern agriculture towards one-crop farming.



































Post a Comment for "What Was The Crop Lien System"